RESEARCHES
Smart Vision & Robotic Sensing

Professor, Robotics Laboratory
Smart Innovation Program, Graduate School of Advanced Science and Engineering
Hiroshima University
Smart Innovation Program, Graduate School of Advanced Science and Engineering
Hiroshima University
Idaku ISHII
- >> Research Contents
- In order to establish high-speed robot senses that are much faster than human senses, we are conducting research and development of information systems and devices that can achieve real-time image processing at 1000 frames/s or greater. As well as integrated algorithms to accelerate sensor information processing, we are also studying new sensing methodologies based on vibration and flow dynamics; they are too fast for humans to sense.
Cardiac Motion Analysis of a Rat Model for Myocardial Infarction
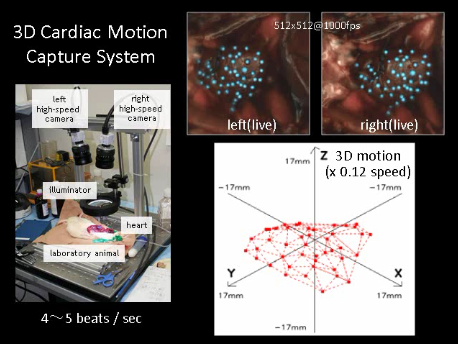
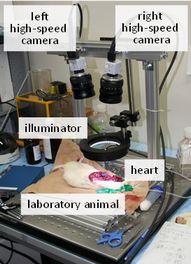 In this study, we develop a cardiac motion capture system
for the open chest of a small laboratory animal.
This system
can capture the three-dimensional (3D) motions of small markers attached to the surface of the heart of an open-chest laboratory animal using high-frame-rate stereo video cameras, which simultaneously captures
8-bit color 512×512 pixel images at 1000 fps from two camera heads.
In this study, we develop a cardiac motion capture system
for the open chest of a small laboratory animal.
This system
can capture the three-dimensional (3D) motions of small markers attached to the surface of the heart of an open-chest laboratory animal using high-frame-rate stereo video cameras, which simultaneously captures
8-bit color 512×512 pixel images at 1000 fps from two camera heads. 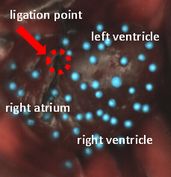
The triangular area assigned with three neighboring markers, are used as its cardiac motion signal to express local expansion/contraction motion. As a quantification index for ischemic heart disease, the rate of change in myocardial area (RCMA) is defined on the basis of the cardiac motion signal, which indicates the myocardium’s activity for a rhythmic expansion/contraction motion in a local area.
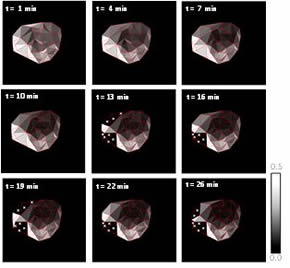
To verify the performance of our cardiac motion capture system, the cardiac motion of a rat model for myocardial infarction is actually quantified as the myocardium’s activity and the time-varying infarction distribution on its heart is visualized using an RCMA map. We analyzed the three-dimensional motion distributions in the heart of a rat model for myocardial infarction, which had heart rate of 4 times/s or greater. In the analysis, the characteristic cardiac motion in ischemic heart diseases was spatiotemporally quantified and it was seen that the infarction area on the heart of the rat caused by ischemia was spread around its left ventricle.
 |
WMV movie(1.9M) captured 3D cardiac motion |
